The CellDEG Technology
-
-
-
- Simple, modular and cost-efficient High Density Cultivators (HDC) and
Photobioreactors for diverse culture volumes - Bubble free gas exchange and turbulent mixing on a vibrating membrane
- Avoidance of photobleaching and photoinhibition
- High quantum yield even at extremely high light intensity
- Ultrahigh Cell Density of cyanobacteria and micro algae in axenic culture
- High potential of the HDC Technology for practical applications of microalgae
and cyanobacteria in the future
- Simple, modular and cost-efficient High Density Cultivators (HDC) and
-
-
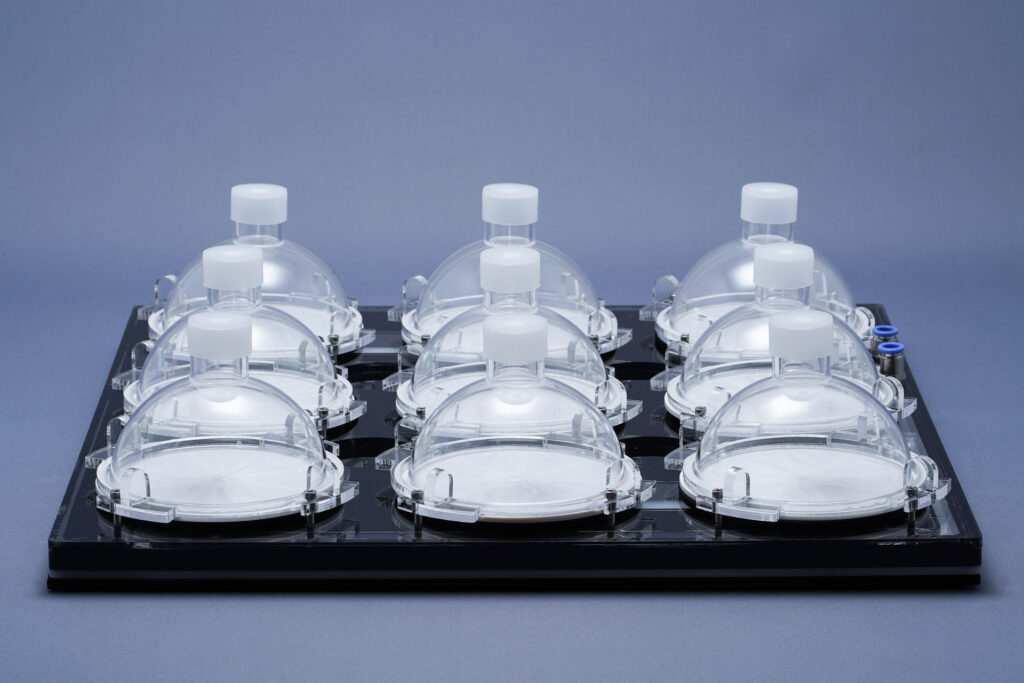
CellDEG provides High-Density Cultivators (HDCs) for microalgae and cyanobacteria
Although microalgae and cyanobacteria can be grown theoretically with much higher yield per irradiated area than crop plants and can be adapted to produce biofuels and other valuable products of photosynthesis, a major problem for their practical and economic applications consists in the low productivities and cell densities obtainable at present in pilot scale photobioreactors. A main reason for the handicap of low cell density in present-date photobioreactors can be seen in the limited use of light in some distance from the irradiated area and sub-optimal turbulent mixing of the culture by the gas-bubble flow.
CellDEG has created a technology for photoautotrophic high-density cultures that enables an extremely efficient use of light with extremely high intensity for the production of biomass or bioproducts in the research and preparative scale.
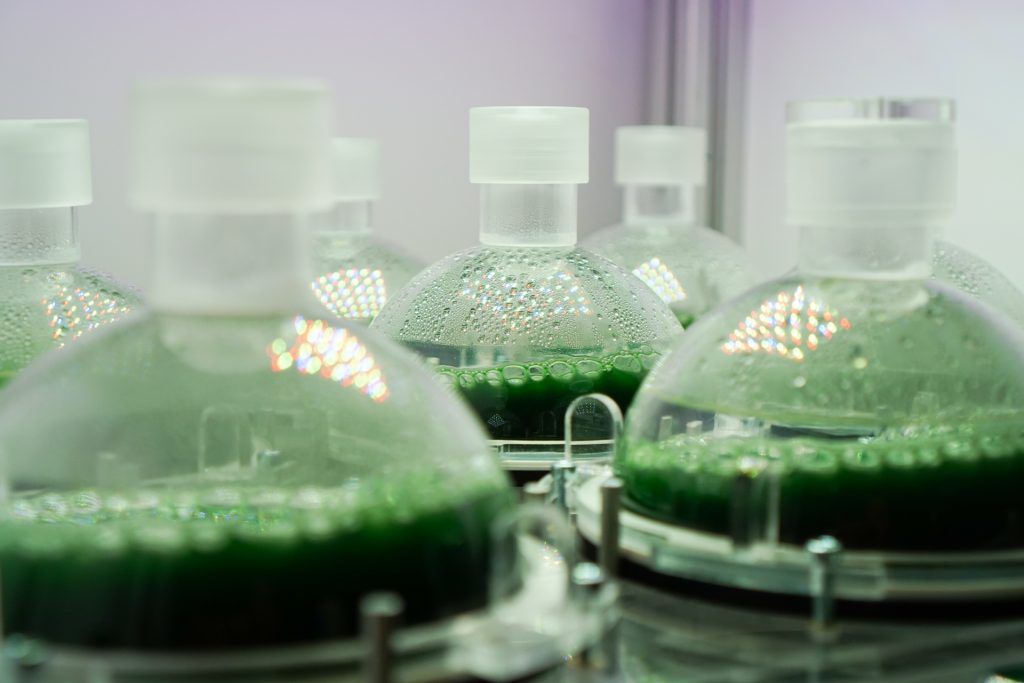
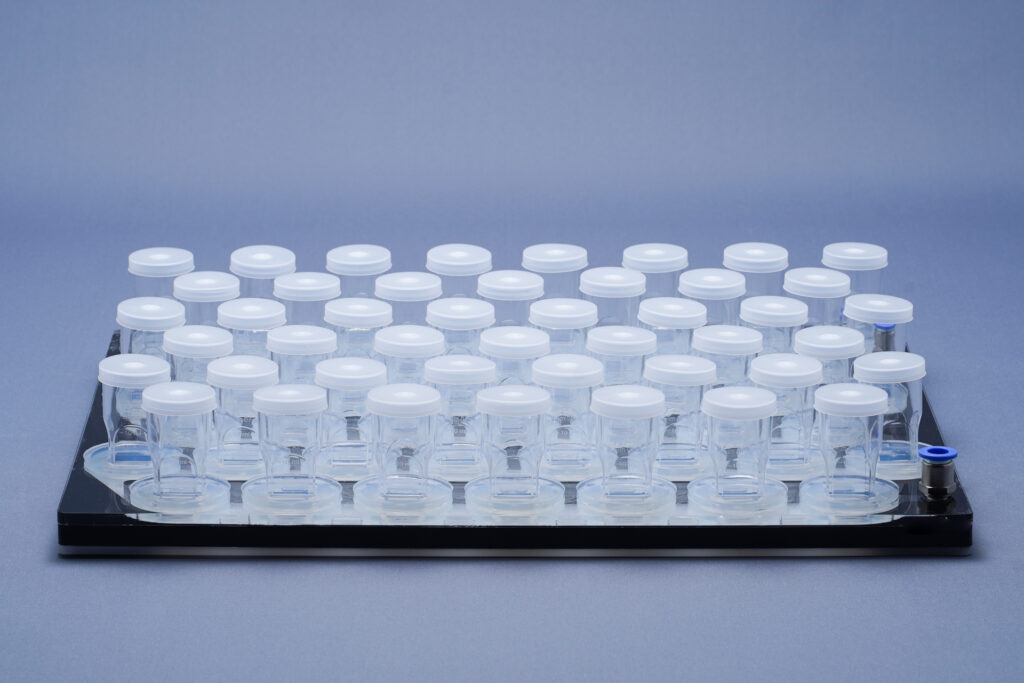
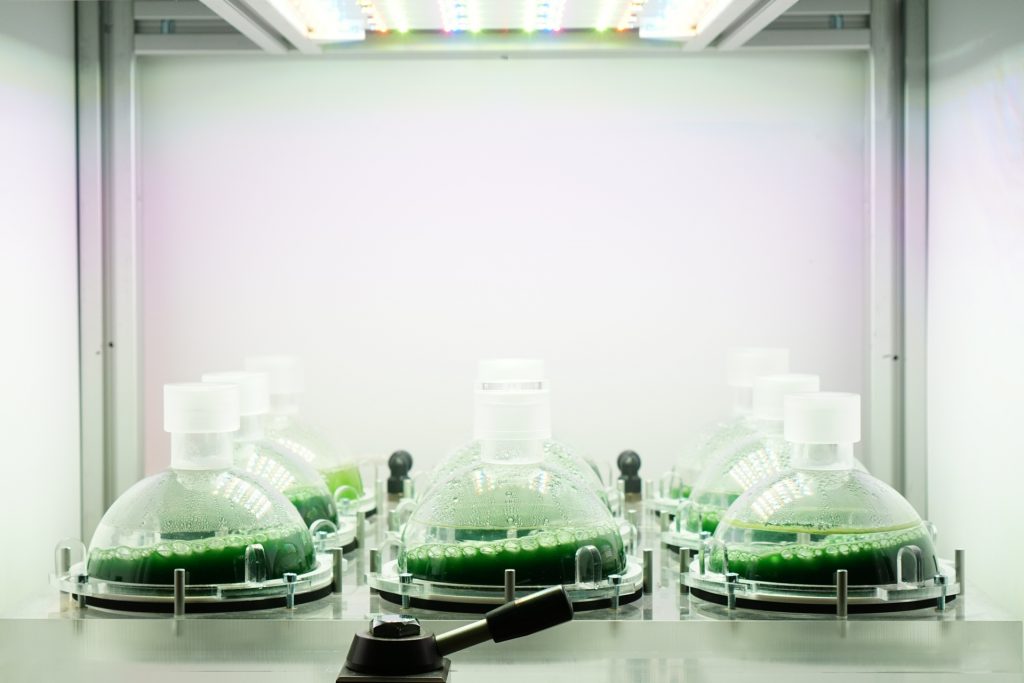
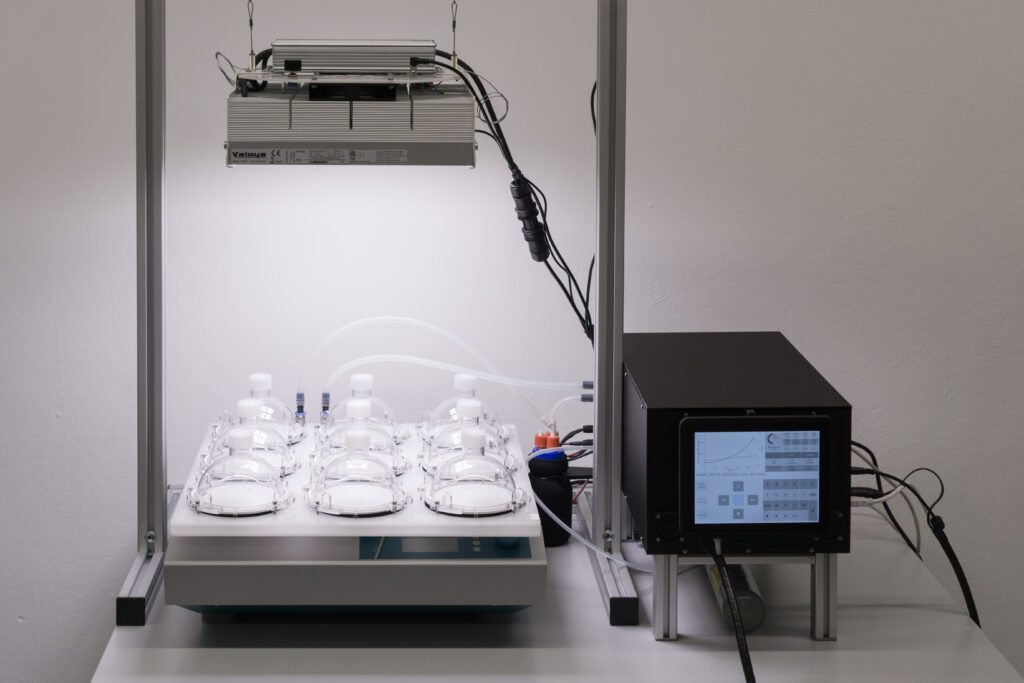
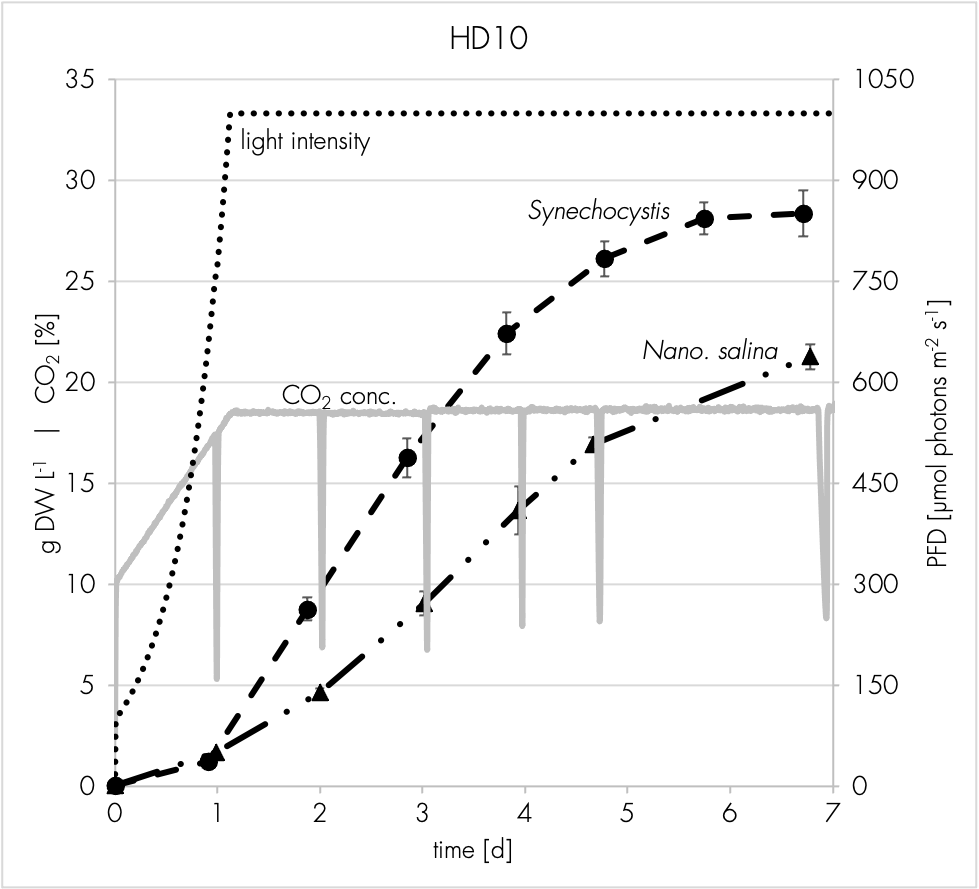
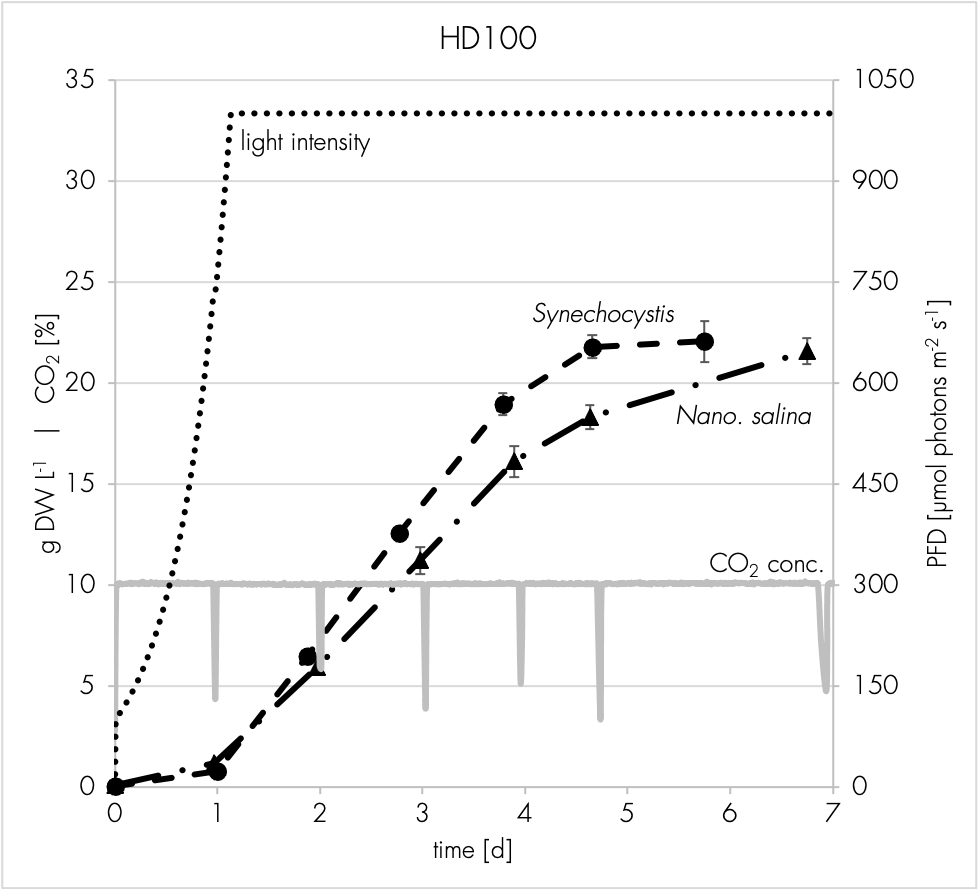
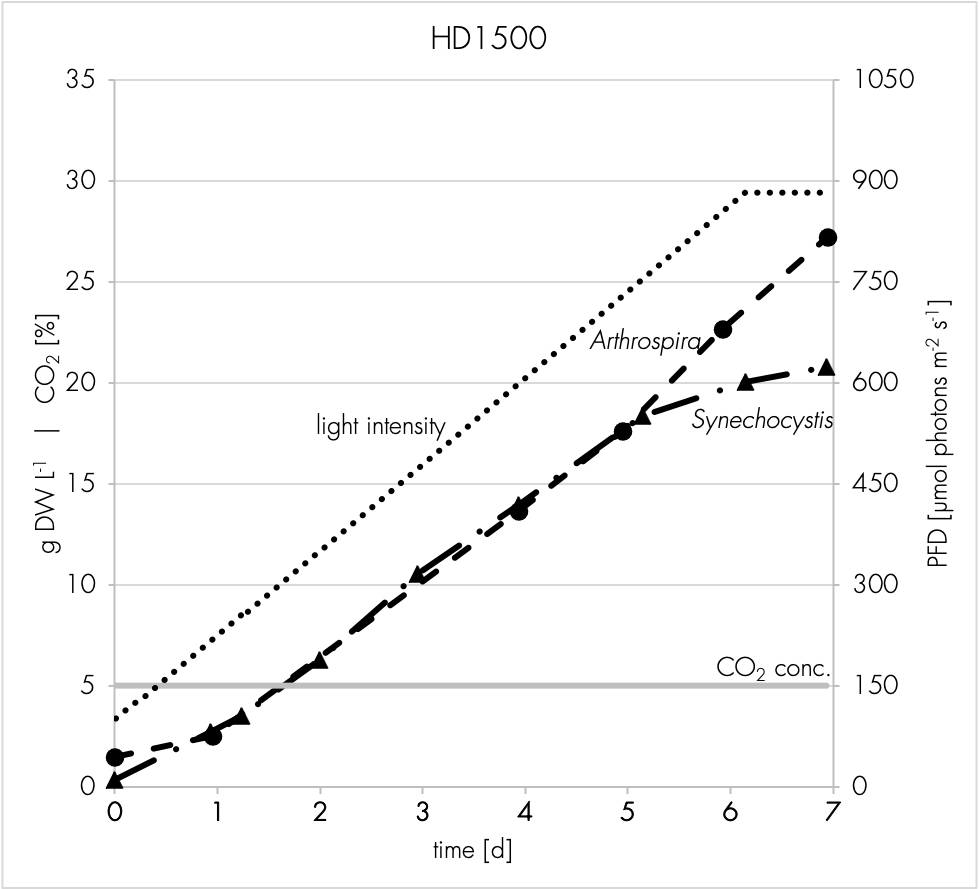
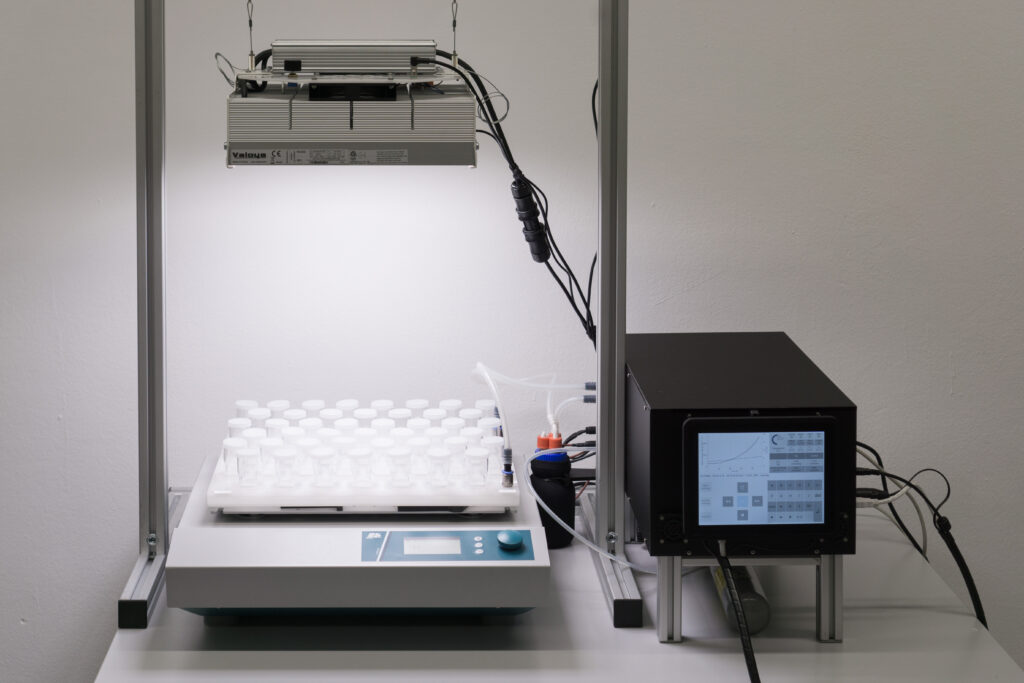
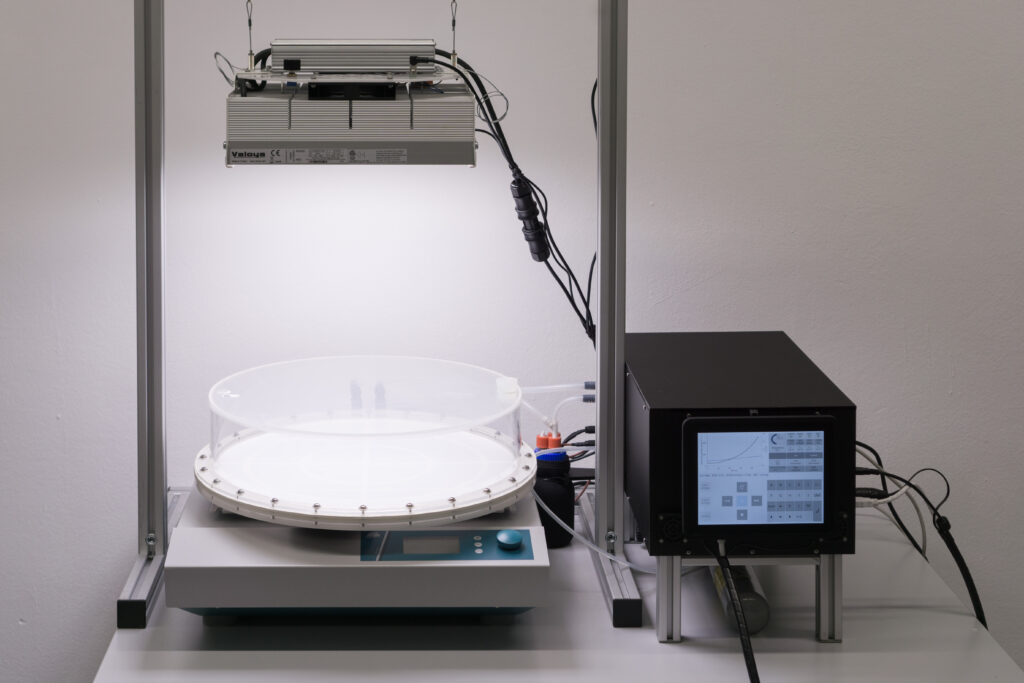
High density cultivators are now available with various culture volumes. The CellDEG technology is basing on bubble-free membrane-mediated CO2 supply combined with the well-known increase of the quantum yield by strong turbulent mixing in high density cultures.
CellDEG´s patented Technology
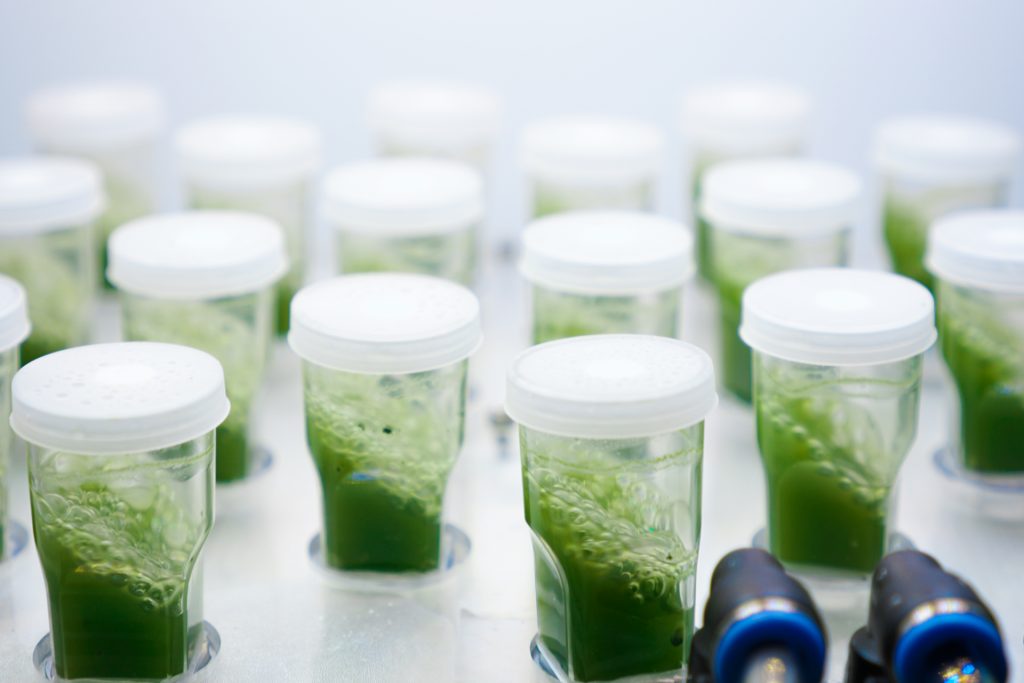
CellDEG provides innovative and flexible systems for axenic culture of cyanobacteria and microalgae. The user-friendly High-Density Cultivators enable rapid growth up to extremely high biomass concentrations. Biomass yields are about 10 times higher than those reached with classic bubble-stream techniques. The cultivators can be easily fitted to very different approaches in microalgae research and bioprocess development.
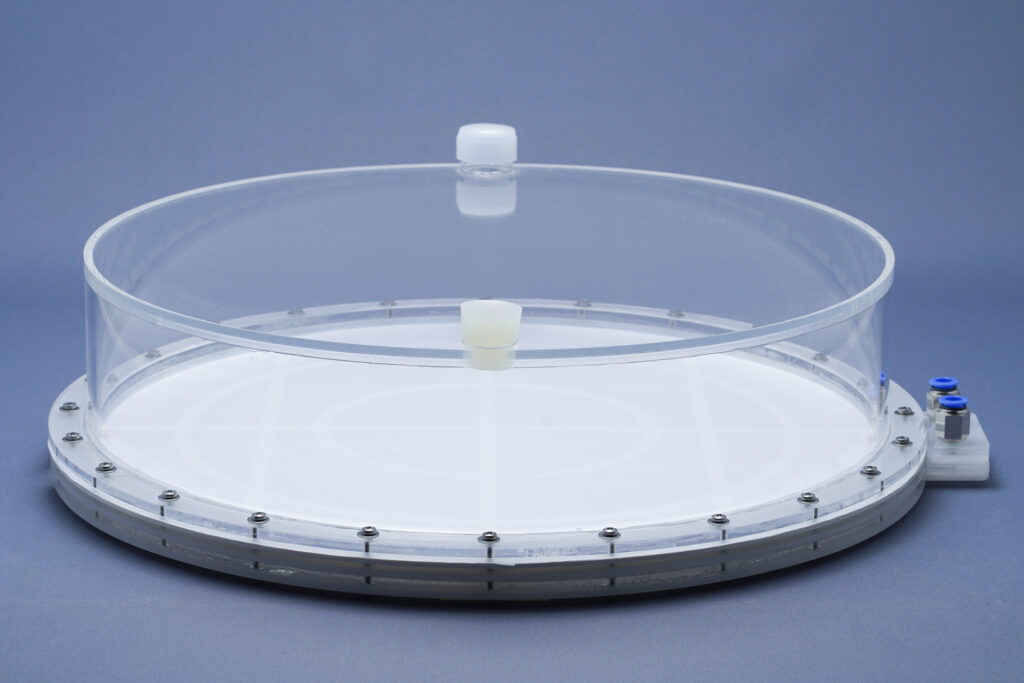
Thin culture layer and membrane mediated CO2 supply. Core elements of the cultivators are two chambers separated by a thin highly gas-permeable membrane of excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strength. The lower chamber contains air enriched with CO2. The CO2 concentration (usually 1-10%) can be maintained by a carbonate buffer (HDC with volume up to 150ml) or by controlled CO2 injection (HDCs with volumes over 150ml). The upper chamber contains the liquid culture and a turbulent gas phase, which is in diffusional exchange with the atmosphere. An oxygen release compartment with defined gas permeability prevents high oxygen partial pressure
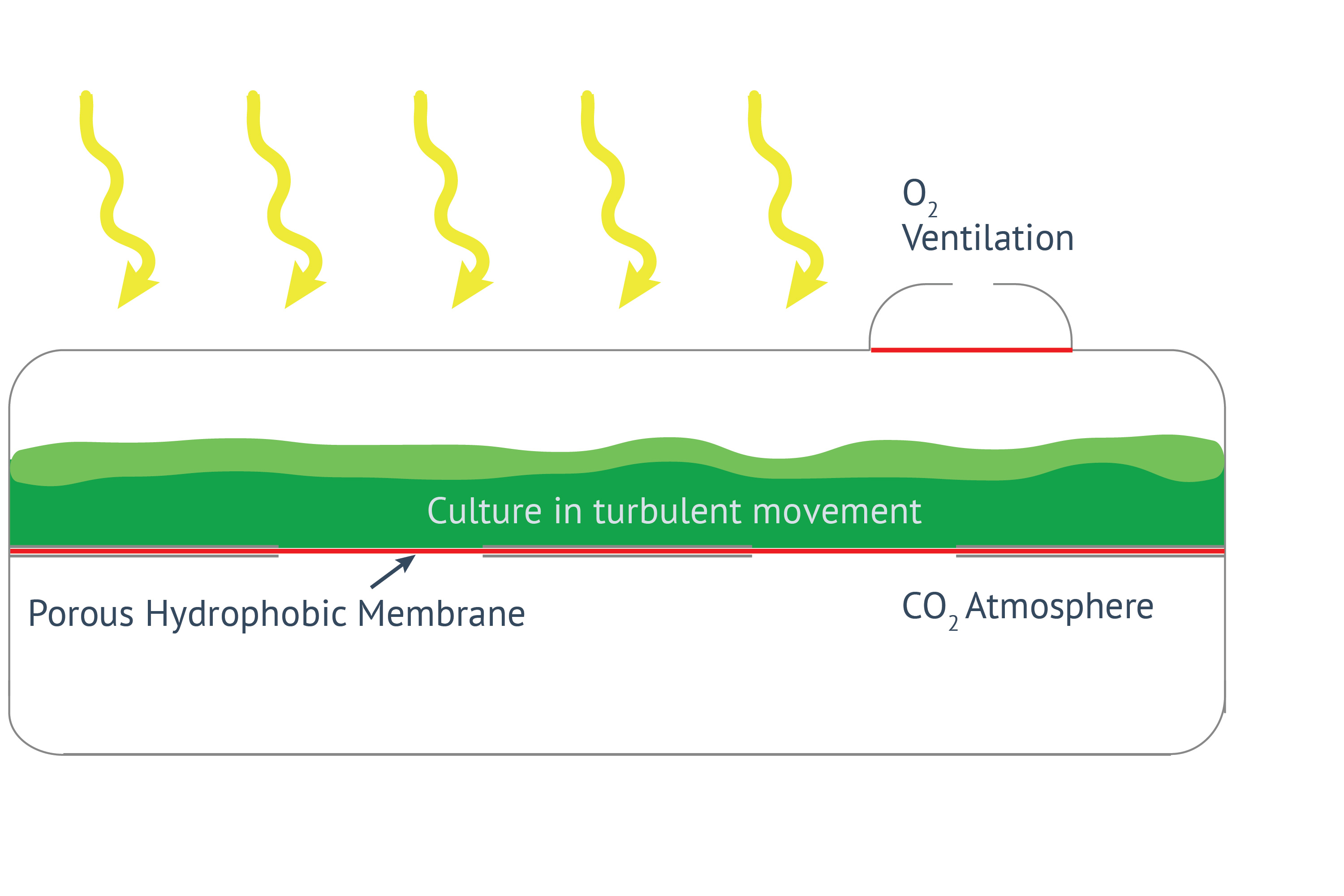
Strong turbulence and high light intensities. In all Celldeg HDCs, turbulence is realized with high frequency orbital shakers which ensure very low shearing stress to the cells. Turbulent liquid flow close to the membrane surface causes an extremely fast bubble-free mass transfer of CO2 into the bulk culture. This prevents CO2 deficiency even at extremely high volumetric rates of carbon assimilation. In addition turbulent mixing of a horizontal thin culture creates an intermittent light regime with short mean durations of the light/dark cycles when the photosynthetic active light only penetrates dense cell cultures 1-2 mm deep. This guarantees a high quantum yield of photosynthesis in the cultivators even at direct solar irradiation or a high intensity of artificial light.
No O2 accumulation. Spatial separation of CO2 supply from oxygen release prevents CO2 loss to the atmosphere. Our HDCs are equipped with a gas exchange compartment separating the turbulent gas space of the culture vessel from the atmosphere. Here, oxygen is released efficiently to the environment by diffusion with only little loss of water vapor. Loss of CO2 to the outer atmosphere is negligible in comparison to its consumption during photosynthesis.
Tested Strains
Cyanobacteria
- Cyanothece PCC 7424
- Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1
- Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
- Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002
- Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942
- Synechococcus elongatus Utex 2973
- Microcystis aeruginosa nies 843
- Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 9432
- Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806
- Nostoc punctiforme
- Nostoc pruniforme
- Nostoc commune
- Nostoc KVJ2
- Nostoc ellipsosporum
Microalgae
- Nannochloropsis salina
- Chlorella sorokiniana
- Scenedesmus rubescens
- Tetraselmis suecica
Moss
- Blasia pusilla